Robert Vogel (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Textbox|boxtype=important|header=Migration from 4.4|text=With BlueSpice 4.5 there were important changes to the container portfolio: # There are no "all-in-one" containers anymore. Neither for FREE, not for PRO and FARM editions # The "distributed-services" setup for PRO and FARM edition has been reworked If you are upgrading from one of the abovementioned setups, please refer to the [[{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Migration_4.4 to 4.5|migration guide]]|icon=yes}} == Overview ==..." Tag: 2017 source edit |
|||
| (84 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | |||
Starting with version 4.5, BlueSpice MediaWiki can be installed with a stack of Docker container images. | |||
Everything is built in a modular way to allow different types of setups. | |||
The most common cases are: | |||
# "All-in-one" (with and without Let's Encrypt) | |||
# Custom database and search service | |||
# Custom load balancer / proxy | |||
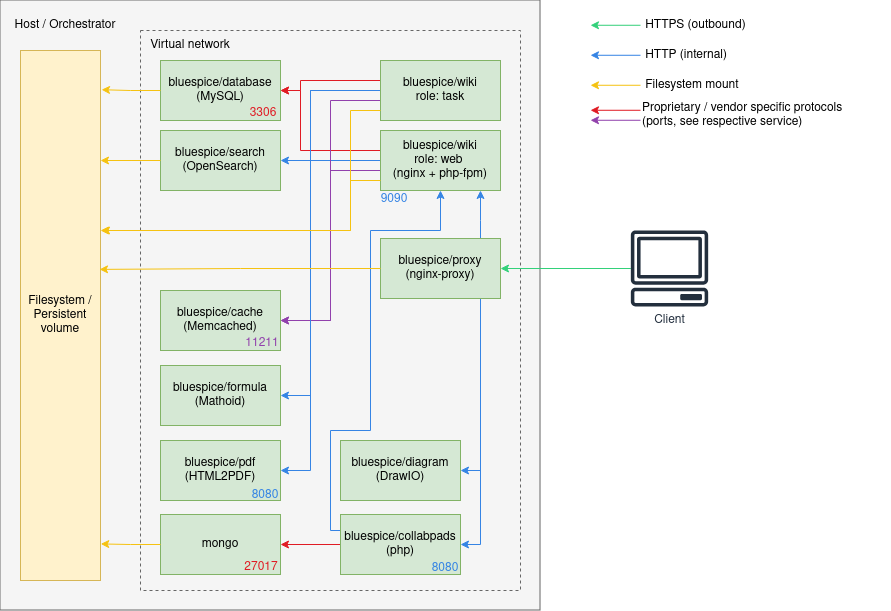
== Architecture == | |||
<drawio filename="Setup:Installation_Guide_Docker-Achitecture" alt="Diagram of BlueSpice Docker Stack Architecture" /> | |||
'''Notes''' | |||
* Internal HTTP connections may use non-standard ports. Those are noted next to the respective services. | |||
** HTTP (in-secure) is only used for internal communication within the virtual network the stack is operated in. All connections to the client use TLS. | |||
* Proprietary ports (esp. for database connections) are noted next to the respective services. | |||
* There may be additional services and ports in use, based on the setup. Some examples: | |||
** When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port <code>636</code>) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> containers to the LDAP-Server | |||
** When using Kerberos authentication, a connection (port <code>88</code>) is used from the <code>bluespice/kerberos-proxy</code> containers to the Kerberos-Server | |||
** When using DeepL or OpenAI services, a HTTPS connection (port <code>443</code>) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> containers to to the respective service | |||
** When using OpenIDConnect authentication, a HTTPS connection (port <code>443</code>) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> "task" container to to the authentication provider | |||
** When using "Let's Encrypt" Certbot, a HTTPS connection (port <code>443</code>) is used from the <code>acme-companion</code> container to the "Let's Encrypt" service | |||
== Step 1: Get the stack == | |||
Load project <code>bluespice-deploy</code> from https://github.com/hallowelt/bluespice-deploy/releases/latest and enter the sub-directory <code>compose</code> for Docker Compose files. | |||
For example, run: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=sh> | |||
wget https://github.com/hallowelt/bluespice-deploy/archive/refs/tags/5.1.1.zip \ | |||
&& unzip 5.1.1.zip \ | |||
&& cd bluespice-deploy-5.1.1/compose | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The directory contains the following files: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
! | ! style="width:375px;" |Filename | ||
! | ! style="" |Type | ||
! | ! style="" |Comment | ||
|- | |||
| style="width:375px;" |<code>bluespice-deploy</code> | |||
| style="" |shell script | |||
| style="" |Start-up script, wrapping command <code>docker compose</code> and service <code>yml</code> files.<br>Additional service <code>yml</code> files can be loaded by adding <code>-f <filename> </code>. | |||
|- | |||
| style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.main.yml</code> | |||
| style="" |yml | |||
| style="" |Main containers of the wiki (<code>wiki-web</code> and <code>wiki-task</code>). | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Containers of database and search services, storing persistent data onto the file system.<br />Optionally with external MySQL/MariaDB and OpenSearch one can skip loading this <code>.yml</code> in <code>bluespice-deploy</code>. Please then wire your services properly in the <code>.env</code> file. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.stateless-services.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Containers for caching, PDF rendering, formula-rendering and diagram editing. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.helper-service.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Helper containers for file system preparation and automated BlueSpice upgrade.<br>These containers exit automatically after finishing tasks. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.proxy.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Container of proxy service. Can be replaced by existing proxy/load-balancer infrastructure. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Additional service for auto-renewal of "Let's Encrypt" certificates.<br>Only required when using the Let's Encrypt service and having no other TLS termination. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml</code> | ||
| | | style="" |yml | ||
| | | style="" |Additional proxy for Kerberos based authentication. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>docker-compose.collabpads-service.yml</code> | ||
| | |yml | ||
| | |Containers of back-end services for [[Manual:Extension/CollabPads|CollabPads]] (included in Pro and Farm editions). | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<code> | | style="width:375px;" |<code>.env.sample</code> | ||
| | | style="" |text | ||
| | | style="" |Sample for creating <code>.env</code> that defines key environment variables. | ||
| | |- | ||
| | | style="width:375px;" |<code>bluespice.service.demo</code> | ||
| style="" |service script | |||
| style="" |Demo-file for control the BlueSpice stack as a <code>systemctl</code> service.<br>One can create e.g a <code>/etc/systemd/system/bluespice.service</code>. | |||
|} | |} | ||
== Step 2: Set up environment variables == | |||
Create your <code>.env</code> based on the sample file <code>.env.sample</code>. | |||
Example: | |||
<pre> | |||
# set or use your data directory | |||
DATADIR=/data/bluespice | |||
VERSION=5.1.1 | |||
EDITION=free | |||
BACKUP_HOUR=04 | |||
WIKI_NAME=BlueSpice | |||
WIKI_LANG=en | |||
WIKI_PASSWORDSENDER=no-reply@wiki.company.local | |||
WIKI_EMERGENCYCONTACT=no-reply@wiki.company.local | |||
WIKI_HOST=wiki.company.local | |||
WIKI_PORT=443 | |||
WIKI_PROTOCOL=https | |||
WIKI_BASE_PATH= | |||
DB_USER=set_or_use_your_db_user_name | |||
DB_PASS=SET_OR_USE_YOUR_DB_PASS_WORD | |||
DB_ROOT_USER=root | |||
DB_ROOT_PASS=$DB_PASS | |||
DB_HOST=database | |||
DB_NAME=bluespice | |||
DB_PREFIX= | |||
SMTP_HOST=mail.company.local | |||
SMTP_PORT=25 | |||
SMTP_USER=... | |||
SMTP_PASS=... | |||
SMTP_ID_HOST=... | |||
LETSENCRYPT=false | |||
</pre> | |||
{{Textbox|boxtype=note|header=Different editions|text=This config works for all editions, but the main image of Pro or Farm edition needs to be obtained differently, see [[{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Pro and Farm edition|Pro and Farm edition]]|icon=yes}} | |||
== Step 3: Start the stack == | |||
Use <code>bluespice-deploy up -d</code> to start the stack. Once all containers are shown as "ready" you can navigate to <code>$WIKI_PROTOCOL://$WIKI_HOST:$WIKI_PORT</code> (e.g. <code><nowiki>https://wiki.company.local</nowiki></code>) in your preferred web browser and start using the application. | |||
When starting the stack the first time, the <code>wiki-task</code> container will automatically perform the installation. It may take a couple of minutes for the process to set up the database and complete. Once it is finished, the password for the default <code>Admin</code> user can be found in <code>$DATADIR/wiki/initialAdminPassword</code>. | |||
== Additional options == | |||
=== Configs for <code>LocalSettings.php</code> === | |||
Instead of exposing the <code>LocalSettings.php</code> for [[mediawikiwiki:Manual:LocalSettings.php|adding additional configurations]], the stack offers two entry points. After the initial installation, you can add your configs to two files in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/</code>: | |||
* <code>pre-init-settings.php</code> - Set configs before the initialization of BlueSpice's debug logging, libraries, skins, extensions and default settings. Configs set here can be picked up by the init process. | |||
* <code>post-init-settings.php</code> - Set configs after the initialization, manipulating configs that have been set by the init process. | |||
For example, if you add the following lines to <code>pre-init-settings.php</code>, you can then read outputted debug logs (if any) in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/logs/debug.log</code>:<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
$GLOBALS['bsgDebugLogGroups']['exception'] = "/data/bluespice/logs/debug.log"; | |||
$wgShowExceptionDetails = true; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Maintenance scripts === | |||
To run [[Setup:Installation Guide/Advanced/Maintenance scripts|maintenance scripts]] from MediaWiki or from other extensions, please use the <code>wiki-task</code> container, which handles all back-end jobs and processes. You can connect into the container in two different ways: | |||
* run <code>./bluespice-deploy exec -it wiki-task bash</code> in the <code>compose</code> directory for Docker Compose files | |||
* or alternatively, run <code>docker exec -it bluespice-wiki-task bash</code> wherever you are on the host machine | |||
Inside the container you can enter the wiki's code base with <code>cd /app/bluespice/w</code> , where one can run scripts like <code>php maintenance/run.php update --quick</code>, <code>php extensions/BlueSpiceExtendedSearch/maintenance/updateWikiPageIndex.php</code> and so on. | |||
=== SSL certificates === | |||
To use a Let's Encrypt certificate for your domain name, set <code>LETSENCRYPT=true</code> in your <code>.env</code> file. | |||
To use a self-signend certificate for your domain name, put its <code>.crt</code> and <code>.key</code> files in <code>${DATADIR}/proxy/certs</code>. For example, with <code>wiki.company.local</code> you should prepare <code>wiki.company.local.crt</code> and <code>wiki.company.local.key</code> files. | |||
=== Kerberos proxy === | |||
For implicit authentication using Kerberos, an additional proxy must be used: <code>bluespice/kerberos-proxy</code> . The file <code>docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml</code> contains a common configuration. It can be used '''instead of''' the regular <code>docker-compose.proxy.yml</code> file inside <code>bluespice-deploy</code> . | |||
Make sure to have the files | |||
* <code>${DATADIR}/kerberos/krb5.conf</code> | |||
* <code>${DATADIR}/kerberos/kerberos.keytab</code> | |||
set up properly. | |||
The file <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/pre-init-settings.php</code> can then be used to set up [[mediawikiwiki:LDAP_hub|"Extension:Auth_remoteuser" and the LDAP stack extensions]]. | |||
=== SAML authentication === | |||
During the initial installation a certificate for message signing will automatically be created. It can be found in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/certs/</code>. | |||
In order to configure a remote IdP, one must copy the IdP metadata XML to a file called <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/saml_idp_metadata.xml</code>. The SP metadata can then be obtained via <code><nowiki>https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/saml/sp/metadata.php/default-sp</nowiki></code>. It must be configured in the remote IdP. | |||
{{Textbox | |||
|boxtype=tip | |||
|header=Test authentication | |||
|text= You can test authentication directly within the SimpleSAMLphp application. To do so, navigate to <code><nowiki>https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/admin</nowiki></code> and log in with <code>admin</code> and the <code>INTERNAL_SIMPLESAMLPHP_ADMIN_PASS</code> found in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/.wikienv</code> | |||
|icon=yes | |||
}} | |||
Next, the extensions "PluggableAuth" and "SimpleSAMLphp" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
wfLoadExtensions( [ | |||
'PluggableAuth', | |||
'SimpleSAMLphp' | |||
] ); | |||
</syntaxhighlight>[[File:Setup:SAML ConfigManager EN 01.png|thumb|300x300px]]to the <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php</code>. Run | |||
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick | |||
to complete the installation. | |||
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in [[Manual:Extension/BlueSpiceConfigManager|Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager]] under "Authentication". | |||
=== OpenID Connect authentication === | |||
The extensions "PluggableAuth" and "OpenIDConnect" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
wfLoadExtensions( [ | |||
'PluggableAuth', | |||
'OpenIDConnect' | |||
] ); | |||
</syntaxhighlight>to the <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php</code>. Run | |||
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick | |||
to complete the installation. | |||
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in [[Manual:Extension/BlueSpiceConfigManager|Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager]] under "Authentication". | |||
[[de:Setup:Installationsanleitung/Docker]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:21, 29 July 2025
Overview
Starting with version 4.5, BlueSpice MediaWiki can be installed with a stack of Docker container images.
Everything is built in a modular way to allow different types of setups.
The most common cases are:
- "All-in-one" (with and without Let's Encrypt)
- Custom database and search service
- Custom load balancer / proxy
Architecture
Notes
- Internal HTTP connections may use non-standard ports. Those are noted next to the respective services.
- HTTP (in-secure) is only used for internal communication within the virtual network the stack is operated in. All connections to the client use TLS.
- Proprietary ports (esp. for database connections) are noted next to the respective services.
- There may be additional services and ports in use, based on the setup. Some examples:
- When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port
636) is used from thebluespice/wikicontainers to the LDAP-Server - When using Kerberos authentication, a connection (port
88) is used from thebluespice/kerberos-proxycontainers to the Kerberos-Server - When using DeepL or OpenAI services, a HTTPS connection (port
443) is used from thebluespice/wikicontainers to to the respective service - When using OpenIDConnect authentication, a HTTPS connection (port
443) is used from thebluespice/wiki"task" container to to the authentication provider - When using "Let's Encrypt" Certbot, a HTTPS connection (port
443) is used from theacme-companioncontainer to the "Let's Encrypt" service
- When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port
Step 1: Get the stack
Load project bluespice-deploy from https://github.com/hallowelt/bluespice-deploy/releases/latest and enter the sub-directory compose for Docker Compose files.
For example, run:
wget https://github.com/hallowelt/bluespice-deploy/archive/refs/tags/5.1.1.zip \
&& unzip 5.1.1.zip \
&& cd bluespice-deploy-5.1.1/compose
The directory contains the following files:
| Filename | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
bluespice-deploy
|
shell script | Start-up script, wrapping command docker compose and service yml files.Additional service yml files can be loaded by adding -f <filename> .
|
docker-compose.main.yml
|
yml | Main containers of the wiki (wiki-web and wiki-task).
|
docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml
|
yml | Containers of database and search services, storing persistent data onto the file system. Optionally with external MySQL/MariaDB and OpenSearch one can skip loading this .yml in bluespice-deploy. Please then wire your services properly in the .env file.
|
docker-compose.stateless-services.yml
|
yml | Containers for caching, PDF rendering, formula-rendering and diagram editing. |
docker-compose.helper-service.yml
|
yml | Helper containers for file system preparation and automated BlueSpice upgrade. These containers exit automatically after finishing tasks. |
docker-compose.proxy.yml
|
yml | Container of proxy service. Can be replaced by existing proxy/load-balancer infrastructure. |
docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml
|
yml | Additional service for auto-renewal of "Let's Encrypt" certificates. Only required when using the Let's Encrypt service and having no other TLS termination. |
docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml
|
yml | Additional proxy for Kerberos based authentication. |
docker-compose.collabpads-service.yml
|
yml | Containers of back-end services for CollabPads (included in Pro and Farm editions). |
.env.sample
|
text | Sample for creating .env that defines key environment variables.
|
bluespice.service.demo
|
service script | Demo-file for control the BlueSpice stack as a systemctl service.One can create e.g a /etc/systemd/system/bluespice.service.
|
Step 2: Set up environment variables
Create your .env based on the sample file .env.sample.
Example:
# set or use your data directory DATADIR=/data/bluespice VERSION=5.1.1 EDITION=free BACKUP_HOUR=04 WIKI_NAME=BlueSpice WIKI_LANG=en WIKI_PASSWORDSENDER=no-reply@wiki.company.local WIKI_EMERGENCYCONTACT=no-reply@wiki.company.local WIKI_HOST=wiki.company.local WIKI_PORT=443 WIKI_PROTOCOL=https WIKI_BASE_PATH= DB_USER=set_or_use_your_db_user_name DB_PASS=SET_OR_USE_YOUR_DB_PASS_WORD DB_ROOT_USER=root DB_ROOT_PASS=$DB_PASS DB_HOST=database DB_NAME=bluespice DB_PREFIX= SMTP_HOST=mail.company.local SMTP_PORT=25 SMTP_USER=... SMTP_PASS=... SMTP_ID_HOST=... LETSENCRYPT=false
Step 3: Start the stack
Use bluespice-deploy up -d to start the stack. Once all containers are shown as "ready" you can navigate to $WIKI_PROTOCOL://$WIKI_HOST:$WIKI_PORT (e.g. https://wiki.company.local) in your preferred web browser and start using the application.
When starting the stack the first time, the wiki-task container will automatically perform the installation. It may take a couple of minutes for the process to set up the database and complete. Once it is finished, the password for the default Admin user can be found in $DATADIR/wiki/initialAdminPassword.
Additional options
Configs for LocalSettings.php
Instead of exposing the LocalSettings.php for adding additional configurations, the stack offers two entry points. After the initial installation, you can add your configs to two files in ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/:
pre-init-settings.php- Set configs before the initialization of BlueSpice's debug logging, libraries, skins, extensions and default settings. Configs set here can be picked up by the init process.post-init-settings.php- Set configs after the initialization, manipulating configs that have been set by the init process.
For example, if you add the following lines to pre-init-settings.php, you can then read outputted debug logs (if any) in ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/logs/debug.log:
$GLOBALS['bsgDebugLogGroups']['exception'] = "/data/bluespice/logs/debug.log";
$wgShowExceptionDetails = true;
Maintenance scripts
To run maintenance scripts from MediaWiki or from other extensions, please use the wiki-task container, which handles all back-end jobs and processes. You can connect into the container in two different ways:
- run
./bluespice-deploy exec -it wiki-task bashin thecomposedirectory for Docker Compose files - or alternatively, run
docker exec -it bluespice-wiki-task bashwherever you are on the host machine
Inside the container you can enter the wiki's code base with cd /app/bluespice/w , where one can run scripts like php maintenance/run.php update --quick, php extensions/BlueSpiceExtendedSearch/maintenance/updateWikiPageIndex.php and so on.
SSL certificates
To use a Let's Encrypt certificate for your domain name, set LETSENCRYPT=true in your .env file.
To use a self-signend certificate for your domain name, put its .crt and .key files in ${DATADIR}/proxy/certs. For example, with wiki.company.local you should prepare wiki.company.local.crt and wiki.company.local.key files.
Kerberos proxy
For implicit authentication using Kerberos, an additional proxy must be used: bluespice/kerberos-proxy . The file docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml contains a common configuration. It can be used instead of the regular docker-compose.proxy.yml file inside bluespice-deploy .
Make sure to have the files
${DATADIR}/kerberos/krb5.conf${DATADIR}/kerberos/kerberos.keytab
set up properly.
The file ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/pre-init-settings.php can then be used to set up "Extension:Auth_remoteuser" and the LDAP stack extensions.
SAML authentication
During the initial installation a certificate for message signing will automatically be created. It can be found in ${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/certs/.
In order to configure a remote IdP, one must copy the IdP metadata XML to a file called ${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/saml_idp_metadata.xml. The SP metadata can then be obtained via https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/saml/sp/metadata.php/default-sp. It must be configured in the remote IdP.
https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/admin and log in with admin and the INTERNAL_SIMPLESAMLPHP_ADMIN_PASS found in ${DATADIR}/wiki/.wikienv
Next, the extensions "PluggableAuth" and "SimpleSAMLphp" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add
wfLoadExtensions( [
'PluggableAuth',
'SimpleSAMLphp'
] );
to the ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php. Run
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick
to complete the installation.
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager under "Authentication".
OpenID Connect authentication
The extensions "PluggableAuth" and "OpenIDConnect" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add
wfLoadExtensions( [
'PluggableAuth',
'OpenIDConnect'
] );
to the ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php. Run
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick
to complete the installation.
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager under "Authentication".